Smarter together in concrete:
one unified data language

The concrete data model
What is it?
A data model is a diagram that shows which data is recorded, in what structure and what relationships exist between the data. The concrete data model is a standard data model for recording data about concrete.
Which data?
There is a lot of concrete data from various parties, such as concrete batching plants, construction companies, research institutes, precast concrete producers and clients.
You can think of data about:
- type of concrete
- properties of the concrete
- composition: which components and how much
- properties of the components
And depending on the situation, data about:
- test methods and results
- location and project information
- execution methods and conditions
The benefits
A standard concrete data model facilitates and promotes the use of data in the concrete industry, both in research as in practice. The data model can be used as a basis for databases and developing applications. It offers various opportunities and possibilities.
Easier collaboration in concrete
A standard concrete data model ensures that everyone uses the same data language and structure, which makes communication and collaboration easier. You can easily combine data from different sources and define which data you do and which you do not want to share.

Supporting sustainability
The concrete industry is moving rapidly towards sustainability. By sharing data we can learn faster together. Concrete does not feel very ‘green’ to many people, but when viewed across its entire life cycle, this is often not justified. Data helps to give an honest picture of concrete.
It is also important that we record which type of concrete is used where, so that we can reuse or recycle it as best as possible after demolition.

Unlocking the power of data and AI
A standard concrete data model makes it easier to share data between different systems and organisations. This way we can create rich data sets with high data quality. This allows us to work with state-of-the-art data techniques, including AI. It opens up possibilities for new insights and applications.

Conceptual concrete data model
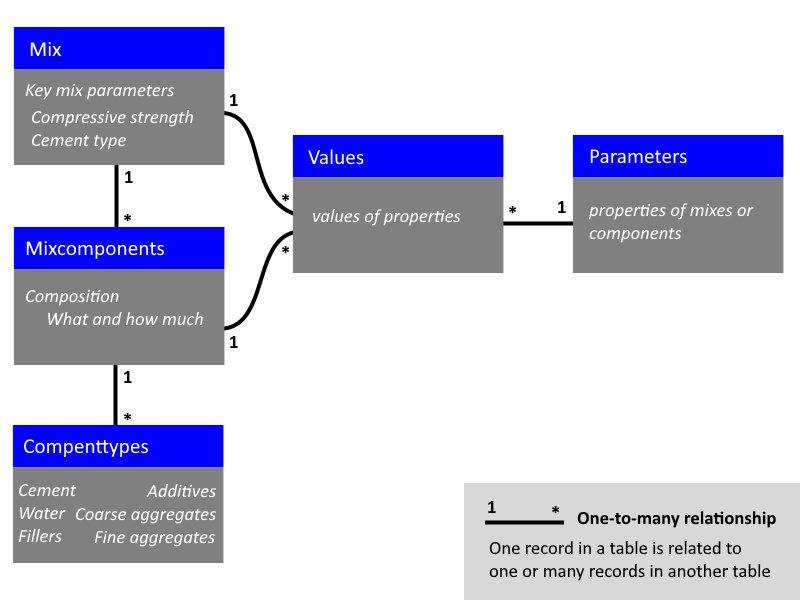
There is not yet a generally accepted and applied concrete data model. However, there are ideas developing and initiatives taken within various organisations. A conceptual idea for the concrete data model is shown below.
Considerations
The mix table is compact and provides the essential information. This contains parameters that are mandatory or highly recommended for each mix.
The distinction between mix and mix components makes it possible to include multiple components of the same type in a mix, for example multiple cement types or multiple aggregates, something that occurs regularly in practice.
The splitting of parameters and values into separate tables makes the data model flexible. The parameter table determines which parameters there are, how they are defined and which unit is used. For simple applications the parameter table can be compact, for complex applications it can be very extensive. The value table gives the value and establishes the relationship between a parameter and a mix or component.
Join
Do you want to use the concrete data model? Do you have ideas, questions or comments? Send an email to contact@concretedatamodel.com.